Archivo: Stoma Opening Closing
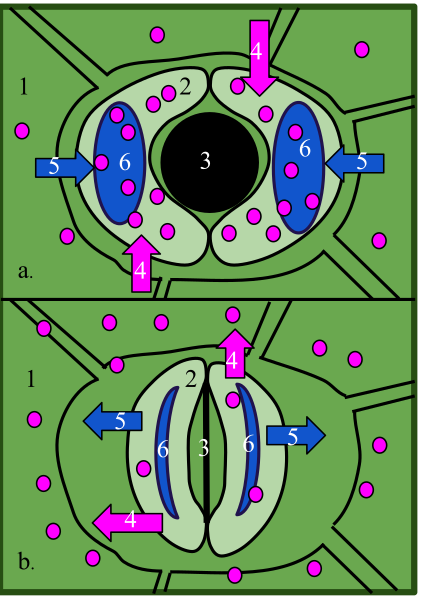
Descripción: Opening and Closing of Stomata 1-Epidermal cell 2-Guard cell 3-Stoma 4-K+ ions 5-Water 6-Vacuole a. Open stoma: stomata are the small pores in the epidermis of leaves. They are bordered by guard cells. The stomata open when the turgor pressure increases in the guard cells, causing the cells to buckle outward. This happens when water flows into the guard cells. Water flows into the guard cells after K+ ions enter the cells, because the water is flowing down its concentration gradient to keep the solute level the same inside the cell as outside. The K+ ions are actively transported into the cells. A proton pump moves H+ ions out of the cell, which is powered by the hydrolysis of ATP. This creates an electrochemical gradient that allows the K+ to flow into the cells through a channel protein. A signal that begins the process is a blue-light component of sunlight. b. Closed stoma: stomata close when the turgor pressure decreases because water exits the cell. The water flows out because the K+ ions exit the cell. They flow out when the proton pump is deactivated. There are a number of signals that can cause stomata to close, these include: a rise in CO2 concentration and the hormone abscisic acid. Even if plants are kept in the dark, the stomata still open and close about every 24 hours, meaning they are regulated by the Circadian rhythms of the plants. The opening and closing of stomata are also influenced by temperature, humidity, and stress.
Título: Stoma Opening Closing
Créditos: Trabajo propio
Autor(a): Lmackay2013
Términos de Uso: Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
Licencia: CC BY-SA 3.0
Enlace de Licencia: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0
¿Se exige la atribución?: Sí
Usos del archivo
La siguiente página enlaza a este archivo:

