Archivo: Marshall PED
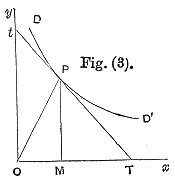
Description: A diagram accompanying Alfred Marshall's original definition of price elasticity of demand. Captioned: The elasticity of demand can be best traced in the demand curve with the aid of the following rule. Let a straight line touching the curve at any point P meet Ox in T and Oy in t, then the measure of the elasticity at the point P is the ratio of PT to Pt. If PT were twice Pt, a fall of 1 per cent. in price would cause an increase of 2 per cent., in the amount demanded; the elasticity of demand would be two. If PT were one-third of Pt, a fall of 1 per cent. in price would cause an increase of 1/3 per cent. in the amount demanded; the elasticity of demand would be one-third; and so on. Another way of looking at the same result is this:—the elasticity at the point P is measured by the ratio of PT to Pt, that is of MT to MO (PM being drawn perpendicular to Om); and therefore the elasticity is equal to one when the angle TPM is equal to the angle OPM; and it always increases when the angle TPM increases relatively to the angle OPM, and vice versâ.
Title: Marshall PED
Credit: Marshall, Alfred. Principles of Economics. Book III, Chapter IV..
Author: Alfred Marshall (died 1924; UK).
Permission: This work is in the public domain in its country of origin and other countries and areas where the copyright term is the author's life plus 70 years or less. This work is in the public domain in the United States because it was published (or registered with the U.S. Copyright Office) before January 1, 1923. This file has been identified as being free of known restrictions under copyright law, including all related and neighboring rights.
Usage Terms: Public domain
License: Public domain
Attribution Required?: No
Usos del archivo
La siguiente página enlaza a este archivo: