Archivo: Faraday emf experiment
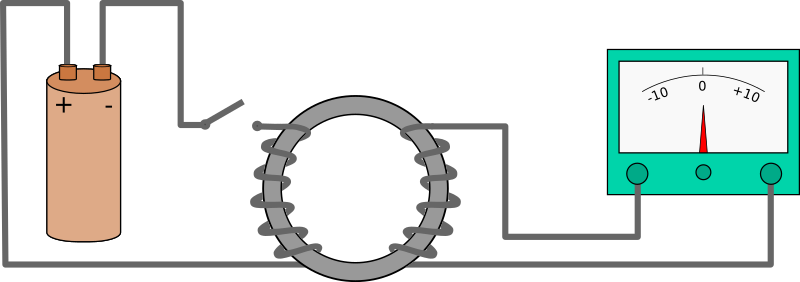
Descripción: Faraday's experiment to try to induce a current from a magnetic field, with a battery on the left, an iron ring in the centre, and a galvanometer on the right. This diagram is based on one found in page 263 of Physics: Principles with Applications, fifth edition, author Douglas C. Giancoli, illustrators Patrice Van Acker and Tamara Newnam Cavallo. The explanation in the book reads as follows, with the left coil being X and the right coil Y: «In his attempt to produce an electric current from a magnetic field, Faraday used an apparatus like that shown in Fig. 21–1. A coil of wire, X, was connected to a battery. The current that flowed through X produced a magnetic field that was intensified by the iron core. Faraday hoped that by using a strong enough battery, a steady current in X would produce a great enough magnetic field to produce a current in a second coil Y. This second circuit, Y, contained a galvanometer to detect any current but contained no battery. He met no success with steady currents. But the long-sought effect was finally observed when Faraday saw the galvanometer in circuit Y deflect strongly at the moment he closed the switch in circuit X. And the galvanometer deflected strongly in the opposite direction when he opened the switch.[...] Faraday concluded that although a steady magnetic field produces no current, a [changing one can]. Such a current is called an induced current.» For more information see Faraday's law of induction and electromagnetic induction.
Título: Faraday emf experiment
Créditos: Trabajo propio
Autor(a): Eviatar Bach
Términos de Uso: Creative Commons Zero, Public Domain Dedication
Licencia: CC0
Enlace de Licencia: http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en
¿Se exige la atribución?: No
Usos del archivo
Las siguientes páginas enlazan a este archivo:

