Archivo: NASA's Aquarius Sees Salty Shifts (8512915213)
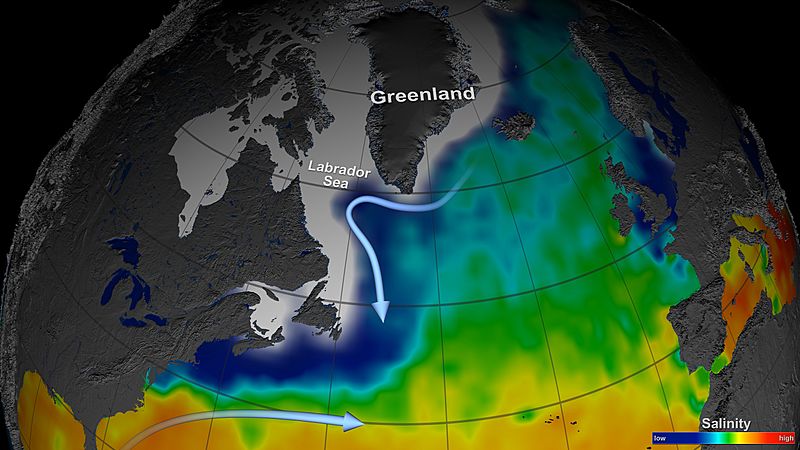
Descripción: The first year of surface salinity measurements from NASA's Aquarius instrument unveils how the seasonal melting of sea ice causes a sharp decrease in sea surface salinity in the Labrador Sea and the coastal waters that surround Greenland. In spring and summer, surface currents transport the low salinity water south, where it meets warmer and saltier water carried north by the Gulf Stream. Launched June 10, 2011, onboard the Argentinian spacecraft Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D, Aquarius is NASA’s first satellite instrument specifically designed to study the salt content of ocean surface waters. Salinity variations, one of the main drivers of ocean circulation, are closely connected with the cycling of freshwater around the planet and provide scientists with valuable information on how the changing global climate is altering global rainfall patterns. To learn more about the Aquarius' first-year discoveries, visit: www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/aquarius/news/data-first-year.... To read more and to view the full lenght video go to: 1.usa.gov/12br9nF NASA image use policy. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. Follow us on Twitter Like us on Facebook Find us on Instagram
Título: NASA's Aquarius Sees Salty Shifts (8512915213)
Créditos: NASA's Aquarius Sees Salty Shifts
Autor(a): NASA Goddard Space Flight Center from Greenbelt, MD, USA
Términos de Uso: Dominio Público
Licencia: Dominio Público
¿Se exige la atribución?: No
Usos del archivo
La siguiente página enlaza a este archivo:

