Archivo: Mechanism of RNA interference
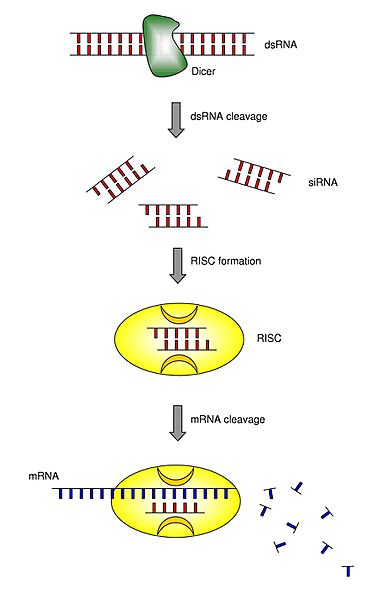
Descripción: Mechanism of RNA interference (RNAi). The appearance of double stranded (ds) RNA within a cell (e.g. as a consequence of viral infection) triggers a complex response, which includes among other phenomena (e.g. interferon production and its consequences) a cascade of molecular events known as RNAi. During RNAi, the cellular enzyme Dicer binds to the dsRNA and cleaves it into short pieces of ~ 20 nucleotide pairs in length known as small interfering RNA (siRNA). These RNA pairs bind to the cellular enzyme called RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) that uses one strand of the siRNA to bind to single stranded RNA molecules (i.e. mRNA) of complementary sequence. The nuclease activity of RISC then degrades the mRNA, thus silencing expression of the viral gene. Similarly, the genetic machinery of cells is believe to utilize RNAi to control the expression of endogenous mRNA, thus adding a new layer of post-transciptional regulation. RNAi can be exploited in the experimental settings to knock down target genes of interest with a high specific and relatively easy technology
Título: Mechanism of RNA interference
Créditos: RNA interference: learning gene knock-down from cell physiology doi:10.1186/1479-5876-2-39
Autor(a): Simone Mocellin and Maurizio Provenzano
Permiso: .mw-parser-output .responsive-license-cc{clear:both;text-align:center;box-sizing:border-box;width:100%;justify-content:space-around;align-items:center;margin:0.5em auto;background-color:#f9f9f9;border:2px solid #e0e0e0;border-spacing:8px;display:flex}.mw-parser-output .responsive-license-cc div{margin:4px}.mw-parser-output .rlicense-text div{margin:0.5em auto}@media screen and (max-width:640px){.mw-parser-output .responsive-license-cc{flex-flow:column}.mw-parser-output .rlicense-text{order:1}} Este archivo está disponible bajo la licencia Creative Commons Atribución 2.0 Genérica. Eres libre: de compartir – de copiar, distribuir y transmitir el trabajo de remezclar – de adaptar el trabajo Bajo las siguientes condiciones: atribución – Debes otorgar el crédito correspondiente, proporcionar un enlace a la licencia e indicar si realizaste algún cambio. Puedes hacerlo de cualquier manera razonable pero no de manera que sugiera que el licenciante te respalda a ti o al uso que hagas del trabajo.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0CC BY 2.0 Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 truetrue
Términos de Uso: Creative Commons Attribution 2.0
Licencia: CC BY 2.0
Enlace de Licencia: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0
¿Se exige la atribución?: Sí
Usos del archivo
La siguiente página enlaza a este archivo:

