Archivo: Lenard window tube labeled
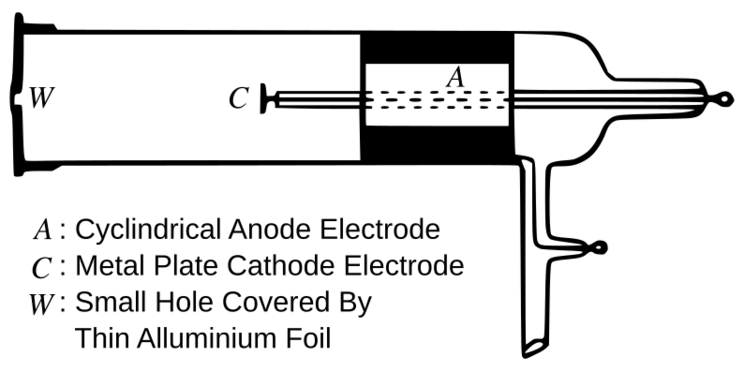
Descripción: Vector depiction of a Crookes tube constructed by German physicist Phillipp Lenard in 1894, which he used to study electrons. It is a partially evacuated glass tube with a metal plate cathode electrode (C) at one end, surrounded by a cylindrical anode electrode (A). Facing the cathode is a small hole in the glass tube covered by a thin aluminum foil (W), just thick enough to keep the atmosphere out, this came to be called a Lenard window. When a high negative voltage of several thousand volts is applied to the cathode, cathode rays (electrons) are projected from the cathode plate. When they hit the thin window, some are able to penetrate and leave the tube into the open air. This convenient source of electrons allowed Lenard to perform experiments determining the penetrating power of electrons. Lenard received the 1905 Nobel prize in physics for this work.
Título: Lenard window tube labeled
Créditos: Trabajo propio, based on
Autor(a): VectorVoyager
Términos de Uso: Creative Commons Zero, Public Domain Dedication
Licencia: CC0
Enlace de Licencia: http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en
¿Se exige la atribución?: No
Usos del archivo
La siguiente página enlaza a este archivo:

